Benefits of Implementing an Environmental Management System
The benefits of an Environmental Management System for your organisation include:
- Strengthened stakeholder confidence – ISO 14001 reduces risk of liability, keeps ahead of legislation and regulatory developments and reduces the environmental burden through elimination, reduction and options
- Greater competitive advantage – your organisation would achieve improved cost control, improved organisational effectiveness and image of organisation
- More secure long term viability – environmental management standard facilitates effective management, demonstrates environmental focus and introduces change in a controlled manner
- Employee involvement and motivation – ISO 14001 demonstrates innovation and forward thinking approach to customers and prospective employees. It clearly defines employees’ functions and establishes environmental awareness and clear methodologies
- As ISO 14001 is an internationally recognised standard, when businesses are operating in numerous locations around the world they can register as 14001 compliant. This eliminates the need for multiple registrations or certifications. ISO 14001 can also reduce trade barriers between registered businesses.
- Other benefits of using ISO 14001:2004 can include reduced cost of waste management, savings in consumption of energy and materials, lower distribution costs, and improved corporate image among regulators, customers and the public.
- Other benefits of ISO 14001 include: strengthened stakeholder confidence, greater competitive advantage, more secure long term viability and employee involvement and motivation


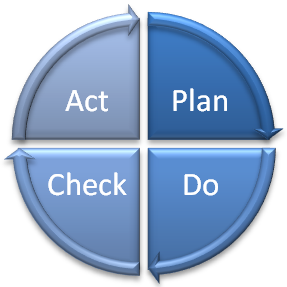 The Plan – Do – Check – Act (PDCA) cycle is the foundation of all ISO management system standards. The cycle ensures development, continuous improvement and control of the management system. The cycle ensures constant monitoring of the organisation’s effectiveness. It consists of the following:
The Plan – Do – Check – Act (PDCA) cycle is the foundation of all ISO management system standards. The cycle ensures development, continuous improvement and control of the management system. The cycle ensures constant monitoring of the organisation’s effectiveness. It consists of the following: